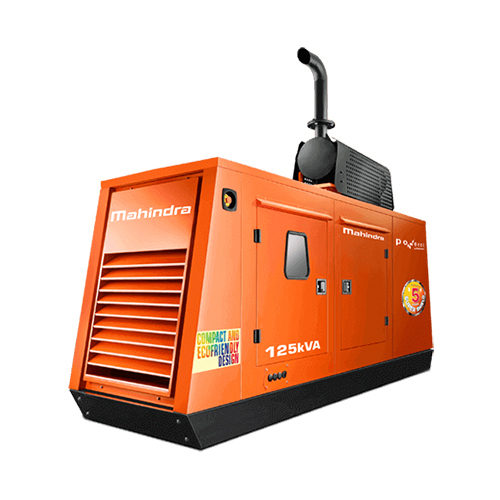
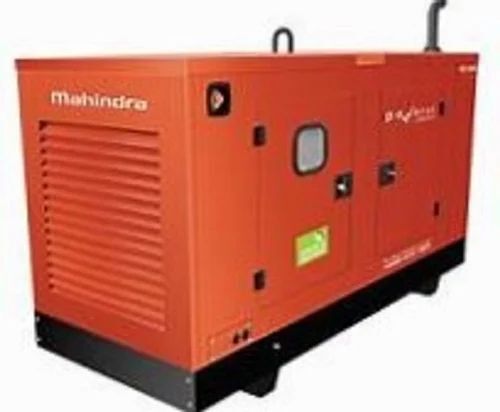
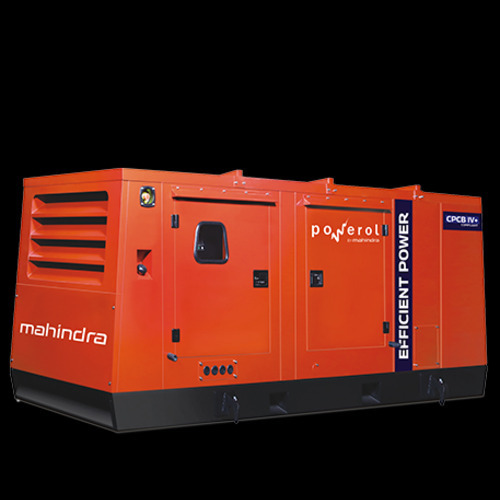
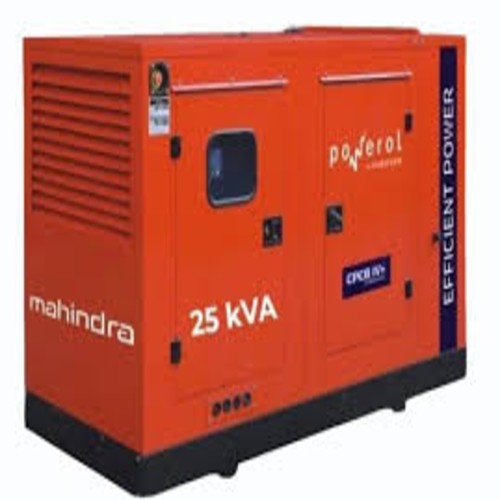
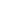
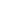
Portable Diesel Generator Supplier in Vadodara
Price 180000 INR/ Unit
MOQ : 1 Unit
Portable Diesel Generator Supplier in Vadodara Specification
- Warranty
- 1 year
- Usage & Applications
- Industrial
- Rated Voltage
- 110-215 Volt (V)
- Phase
- 3
- Material
- MS
- Features
- Good Quality
- Frequency
- 50-60 Hertz (HZ)
About Portable Diesel Generator Supplier in Vadodara
FAQs of Portable Diesel Generator Supplier in Vadodara:
Q: What is the frequency range of the Portable Diesel Generator?
A: The frequency range of the Portable Diesel Generator is 50-60 Hertz (HZ).Q: Is the generator suitable for outdoor usage?
A: Yes, the generator is outdoor-rated with an IP65 rating.Q: What is the rated voltage of this generator?
A: The rated voltage of the generator is 110-215 Volt (V).Q: What type of material is used in the construction of this generator?
A: The generator is made of MS (Mild Steel).Q: What is the warranty duration for this generator?
A: The generator comes with a warranty of 1 year.Q: Is the generator designed for industrial applications?
A: Yes, the Portable Diesel Generator is specifically designed for industrial usage and applications.Q: What phase does the generator operate on?
A: The generator operates on 3-phase power.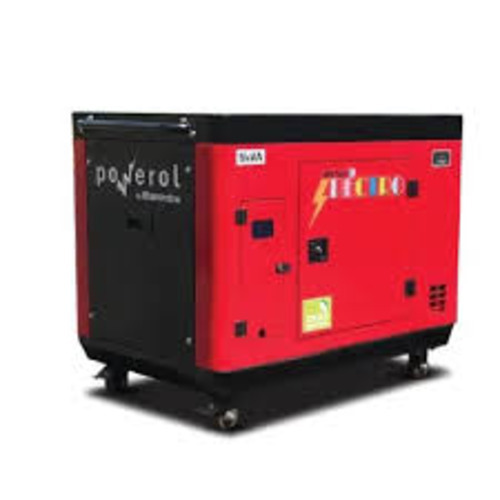
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Diesel Generator Category
82.5 to 200 kVA Diesel Generator
Price 1000000.0 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Warranty : Yes
Product Type : Diesel Generator
Diesel Generator Set 5 to 320 KVA Mahindra Power
Price 2500000.0 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Warranty : 1 year
Features : Good Quality
Material : MS
Mahindra Diesel Generator
Price 500000 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Unit
Warranty : 1 year
Features : Good Quality
Product Type : Mahindra Diesel Generator
Material : MS

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry